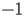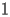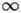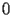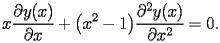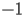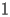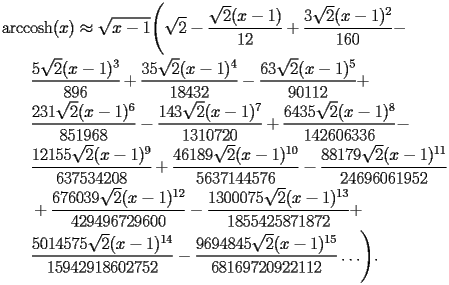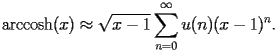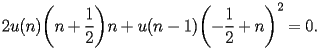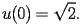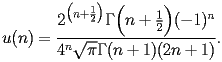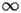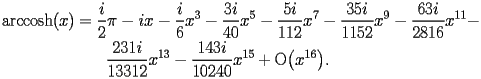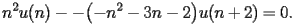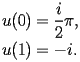HACS Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine
HACS.1 Introduction |
top up back next into bottom |
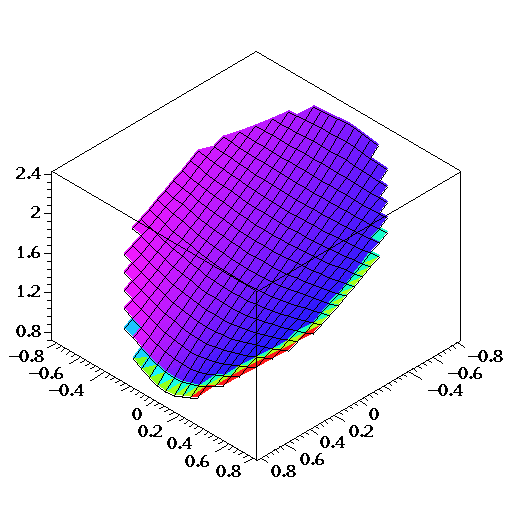
Let
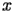 be a complex variable of
be a complex variable of
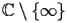 .The function Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine (noted
.The function Inverse Hyperbolic Cosine (noted
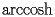 ) is defined by the following second order differential equation
) is defined by the following second order differential equation
| HACS.1.1 |
The initial conditions of HACS.1.1 are given at
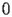 by
by
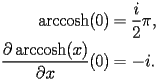
|
HACS.1.2 |
Related functions: Inverse Cosine,Inverse Sine
HACS.2 Series and asymptotic expansions |
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.1 Asymptotic expansion at
|
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.1.1 First terms |
top up back next into bottom |
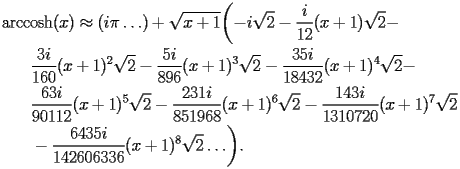
|
HACS.2.1.1.1 |
HACS.2.1.2 General form |
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.2 Asymptotic expansion at
|
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.2.2 General form |
top up back next into bottom |
| HACS.2.2.2.1 |
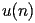 satisfy the recurrence
satisfy the recurrence
| HACS.2.2.2.2 |
| HACS.2.2.2.3 |
| HACS.2.2.2.4 |
HACS.2.3 Asymptotic expansion at
|
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.3.1 First terms |
top up back next into bottom |
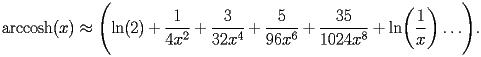
|
HACS.2.3.1.1 |
HACS.2.3.2 General form |
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.4 Taylor expansion at
|
top up back next into bottom |
HACS.2.4.2 General form |
top up back next into bottom |
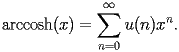
|
HACS.2.4.2.1 |
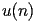 satisfy the recurrence
satisfy the recurrence
| HACS.2.4.2.2 |
| HACS.2.4.2.3 |